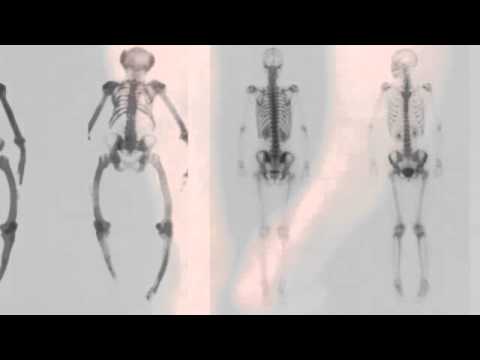
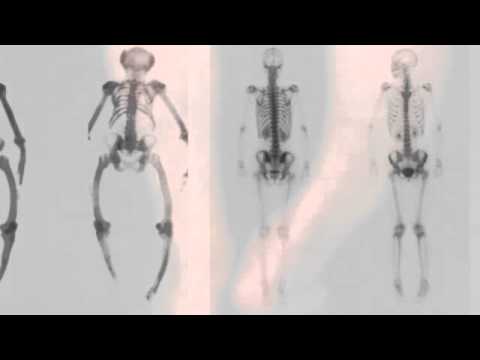
Paget’s disease of bone disrupts the normal cycle of bone renewal, causing bones to become weakened and possibly deformed.
It’s a fairly common condition in the UK, particularly in older people. It’s rare in people under 50 years of age.
There are treatments that can help keep it under control for many years, but it can cause persistent pain and a range of other problems in some people.
Symptoms of Paget's disease of bone
Paget's disease of bone can affect one or several bones. Commonly affected areas include the pelvis, spine and skull.
Symptoms can include:
constant, dull bone pain
joint pain, stiffness and swelling
a shooting pain that travels along or across the body, numbness and tingling, or loss of movement in part of the body
But in many cases there are no symptoms and the condition is only found during tests carried out for another reason.
Read more about the symptoms of Paget's disease of bone.
When to see your GP
See your GP if you have:
persistent bone or joint pain
deformities in any of your bones
symptoms of a nerve problem, such as numbness, tingling or loss of movement
Your GP can organise tests to check your bones and look for problems such as Paget's disease of bone.
Read more about how Paget's disease of bone is diagnosed.
Causes of Paget's disease of bone
Bone cells regenerate in a similar way to skin - old bone is removed and replaced by new bone. This is known as bone remodelling.
Two cells are responsible for this:
osteoclasts - cells that absorb old bone
osteoblasts - cells that make new bone
In Paget's disease of bone, something goes wrong with the osteoclast cells and they start to absorb bone at a much faster rate than usual.
The osteoblasts then try to produce new bone more quickly, but the new bone is larger and weaker than normal.
It's not clear what triggers this, but you're at a higher risk if you have a family history of Paget's disease of bone. You may inherit a genetic fault that means you're much more likely to develop the condition.
Treatments for Paget's disease of bone
There's currently no cure for Paget's disease of bone, but treatment can help relieve the symptoms.
If you don't have any symptoms, your doctor may suggest keeping an eye on your condition and delaying treatment until any problems occur.
The main treatments are:
bisphosphonate medication - medicines that help control bone regeneration
painkillers - usually over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen
supportive therapies - including physiotherapy, occupational therapy and devices such as walking sticks or shoe inserts
surgery - this may be needed if further problems develop, such as fractures, deformities or severe joint damage
Ensuring you get enough calcium and vitamin D can also help. Some people may need to take supplements.
Read more about how Paget's disease of bone is treated.
Further problems caused by Paget's disease of bone
Paget's disease of bone can sometimes lead to further, potentially serious problems.
These include:
fragile bones that break more easily than normal
enlarged or misshapen bones
permanent hearing loss (if the skull is affected)
too much calcium in the blood
heart problems
in rare cases, bone cancer
Read more about possible complications of Paget's disease of bone.
Other types of Paget's disease
In addition to Paget's disease of bone, there are several other types of Paget's disease.
These include:
Paget's disease of the breast or nipple - a rare type of breast cancer
Paget's disease of the penis - a rare type of penile cancer
Paget's disease of the vulva - a rare type of vulval cancer
The general term "Paget's disease" is sometimes used to refer to Paget's disease of bone.