The symptoms of an MRSA infection will depend on what part of the body is infected.
Skin and soft tissue MRSA infections
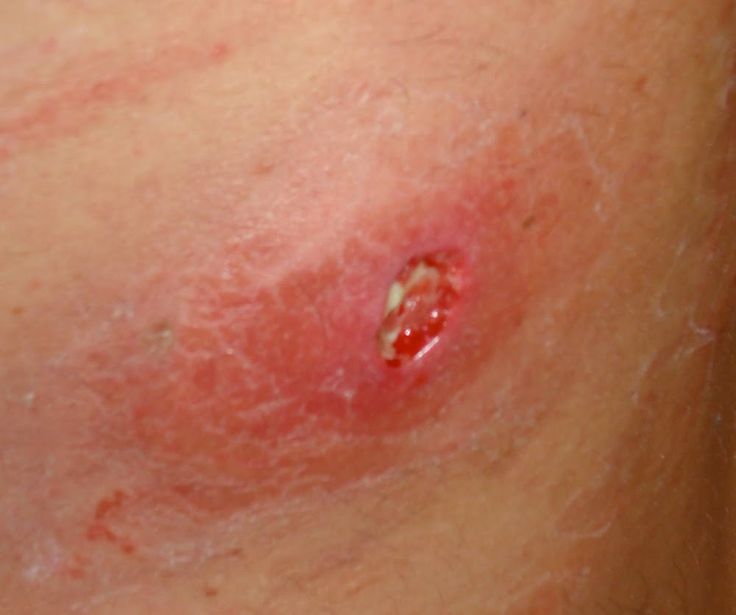
If MRSA infects the skin, it can result in a wound infection, boil or abscess.
If it infects the deeper layers of skin, it’s known as cellulitis.
Typical symptoms are:
redness
swelling
tenderness
pain
a discharge of pus
Some people have additional symptoms, such as a high temperature (fever) and a general feeling of being unwell.
These infections can also be caused by bacteria other than MRSA, so having the symptoms above doesn’t necessarily mean you have MRSA.
Invasive MRSA infections
If the MRSA bacteria penetrate deeper inside your body or into your blood, they can cause a more serious, invasive infection.
Signs of an invasive infection include:
a high temperature of 38C (100.4F) or above
chills
generally feeling unwell
confusion
muscle aches and pains
pain, swelling and tenderness in the affected body part
Examples of invasive MRSA infections include:
blood poisoning (sepsis) – which could lead to septic shock, where your blood pressure drops to a dangerously low level
urinary tract infection (UTI) – infection of the tubes through which urine passes
endocarditis – infection of the heart valves
pneumonia – a lung infection
septic bursitis – inflammation of a fluid-filled sac that forms under the skin (usually over a joint)
septic arthritis – a joint infection
osteomyelitis – a bone infection
Click on the links above for the specific symptoms of these infections.