A to Z of Medical Conditions
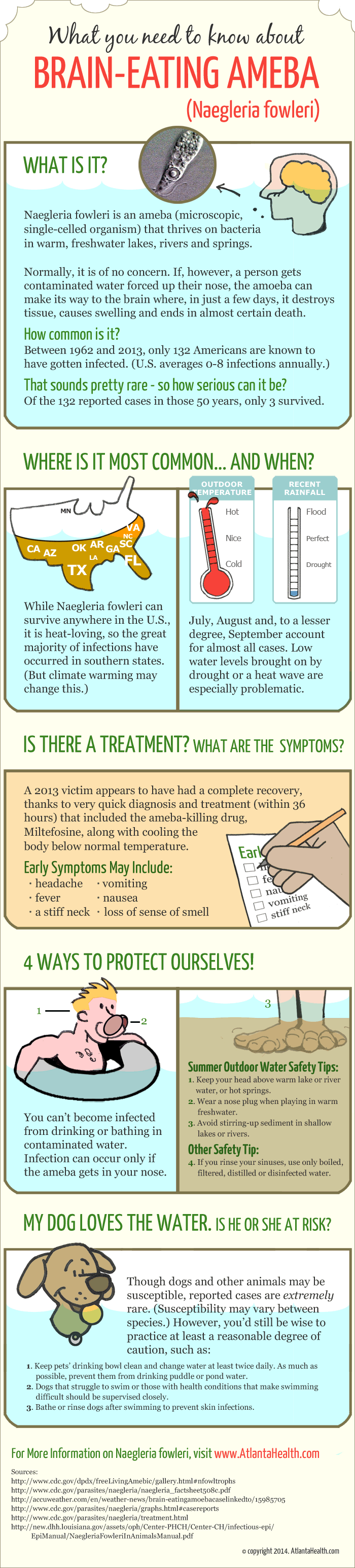
What you need to know about BRAIN-EATING AMEBA (Naegleria fowleri)
Naegleria fowleri is an ameba (microscopic, single-celled organism) that thrives on bacteria in warm, freshwater lakes, rivers and springs.
Normally, it is of no concern. If, however, a person gets contaminated water forced up their nose, the amoeba can make its way to the brain where, in just a few days, it destroys tissue, causes swelling and ends in almost certain death.
A Patient’s Guide to Scoliosis
The spine is supposed to go straight up and down vertically. When people have scoliosis, the spine curves from side to side and may look like a “C” or an “S”. You can learn more by viewing this Houston minimally invasive spine treatment infographic.
What are the signs of spinal stenosis?
What are the signs of spinal stenosis?
Get more info here.
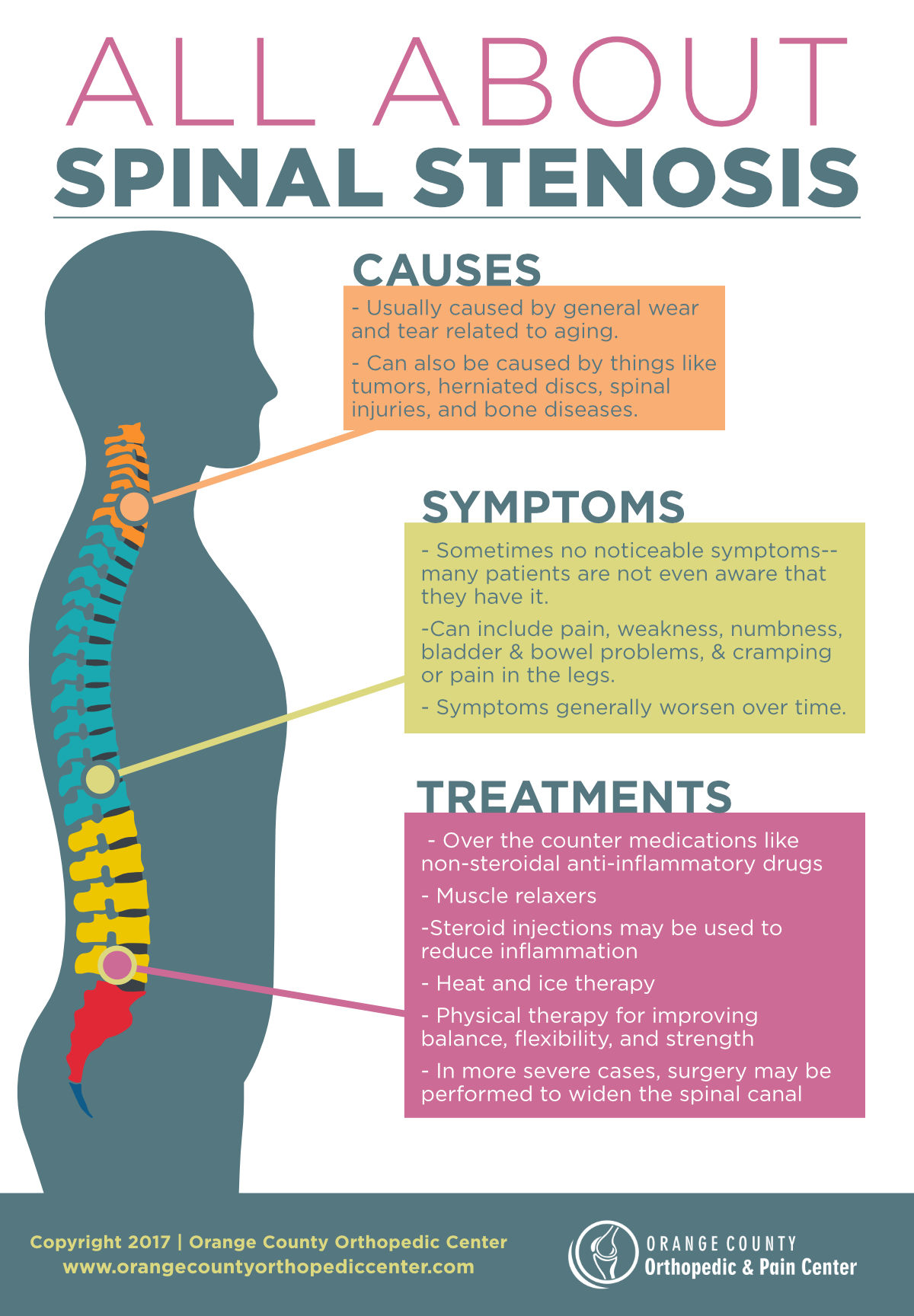
Causes:
Usually caused by general wear and tear related to aging. Can also be caused by things like tumors, herniated discs, spinal injuries, and bone diseases.
Symptoms:
Sometimes no noticeable symptoms many patients are not even aware that they have it. Can include pain, weakness, numbness, bladder & bowel problem, & cramping or pain in the legs. Symptoms generally worsen over time.
Sciatica – Check if you have sciatica
Sciatica is when the sciatic nerve, which runs from your hips to your feet, is irritated. It usually gets better in 4 to 6 weeks but can last longer.
Check if you have sciatica
If you have sciatica, your:
bottom
backs of your legs
feet and toes
may feel:
painful – the pain may be stabbing, burning or shooting
tingling – like pins and needles
numb
weak
Your symptoms may be worse when moving, sneezing or coughing.
You may also have back pain, but this isn’t usually as bad as the pain in your bottom, legs or feet.
You probably don’t have sciatica if you only have back pain.
How you can ease the pain yourself
Sciatica usually gets better in 4 to 6 weeks but can sometimes last longer.
To help relieve your pain and speed up your recovery:
Do
carry on with your normal activities as much as possible
regular back stretches
start gentle exercise as soon as you can – anything that gets you moving can help
hold heat packs to the painful areas – you can buy these from pharmacies
ask your pharmacist about painkillers that can help
Don’t
sit or lie down for long periods – even if moving hurts, it’s not harmful and can help you get better faster
take paracetamol on its own – this doesn’t help with back pain or sciatica
use hot water bottles to ease the pain – you could scald yourself if your skin is numb
See a GP if the pain:
hasn’t improved after trying home treatments for a few weeks
is getting worse
is stopping you doing your normal activities
Go to A&E/ER if you:
have sudden weakness in both legs
have numbness or tingling around and under your genitals or inner thighs
suddenly can’t pee, or can’t control when you pee or poo
These could be symptoms of a serious back problem that needs to be treated in hospital as soon as possible.
Treatments from a GP
Your GP may:
suggest exercises and stretches
prescribe painkillers that help with nerve pain like sciatica
They might also refer you for:
physiotherapy – including exercise advice and techniques like massage (manual therapy)
psychological support – to help you cope with the pain
Physiotherapy from the NHS may not be available everywhere and waiting times can be long. You can also get it privately.
Injections and surgery for sciatica
How to stop sciatica coming back
To reduce the chances of getting sciatica again:
Do
stay active – take regular exercise
use a safe technique when lifting heavy objects
make sure you have a good posture when sitting and standing
sit correctly when using a computer
lose weight if you’re overweight
Don’t
- smoke – smoking can increase your risk of getting sciatica
Causes of sciatica
Sciatica is due to something pressing or rubbing on the sciatic nerve.
Causes include:
a slipped disc (the most common cause) – when a soft cushion of tissue between the bones in your spine pushes out
spinal stenosis – narrowing of the part of your spine where nerves pass through
spondylolisthesis – when one of the bones in your spine slips out of position
a back injury